Fused Testing – The Best of All Worlds

What company hasn’t been torn between different test strategies and methodologies? With fused testing strategies, you can reap the benefits of methods historically depicted as incompatible. Not just automated vs. manual strategies but dedicated test teams vs. on-demand testers. Beyond that, fused testing integrates your DevOps systems tighter with your QA systems, allowing you to drive new testing based on DevOps feedback.
This pillar page will dive deeper into how you can perform fused testing and why it’s crucial to modern QA success. But first, we’ll start with a general definition.
Table of Contents
- What is Fused Software Testing?
- When to use automation
- Automated testing challenges
- When to use manual testing
- Manual testing challenges
- On-demand and full-time staffing models
- Benefits of fused testing
- Fused testing use cases
- Building blocks of fused software testing
- Fused Testing APIs
- More Resources
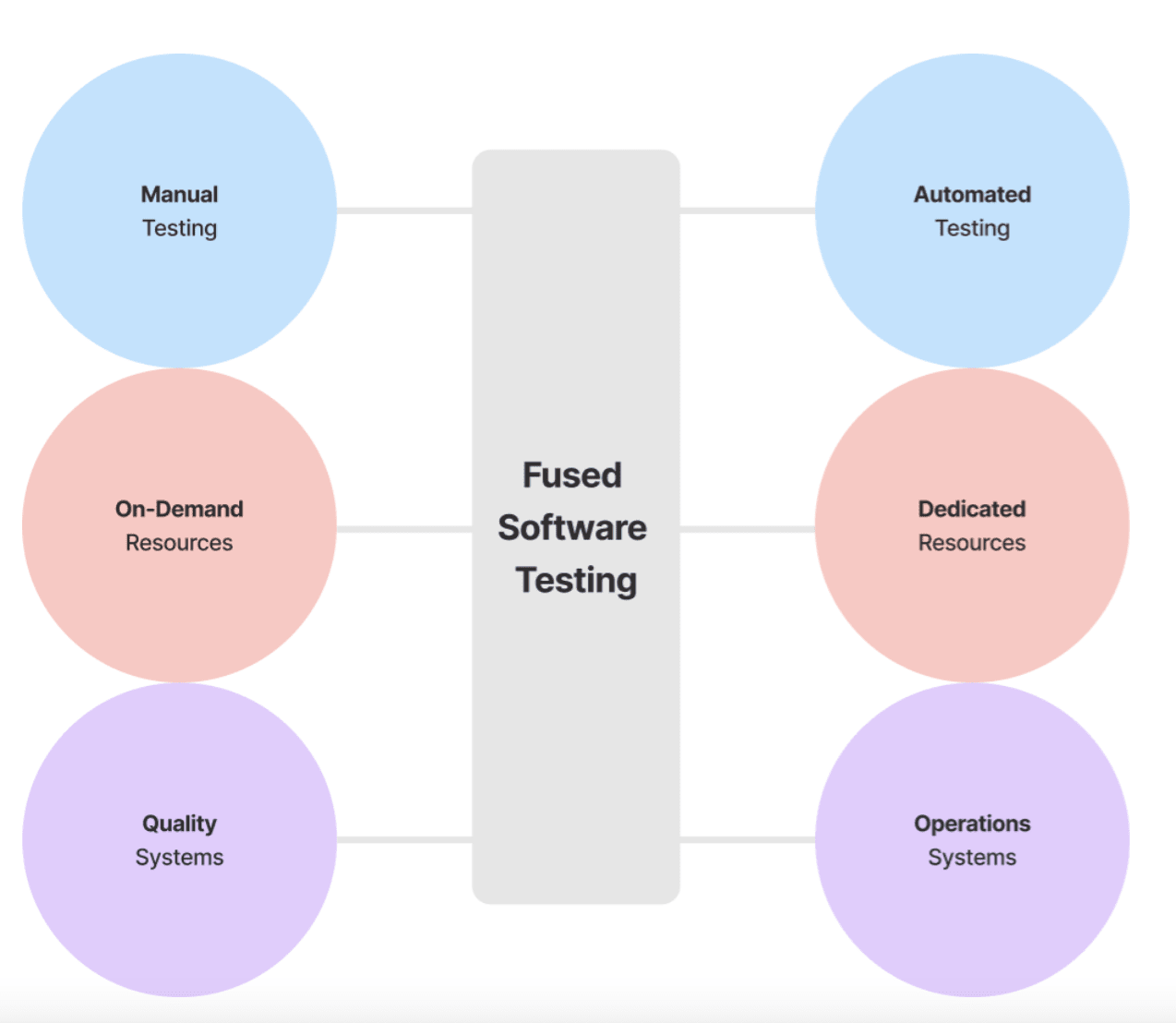
What is Fused Software Testing?
The basic concept behind fused software testing is to combine pairs of concepts that traditionally have been in opposition. Historically, automated and manual testing has been considered separately, but fused testing combines them to support and reinforce one another. It also cuts through the false dichotomy of on-demand or dedicated testers by providing some dedicated testers with the opportunity to deliver additional testers for burstable testing over a short period. Finally, it integrates operational systems (DevOps) with quality systems to allow testing to focus on areas DevOps identifies as needing extra attention.
Fused testing aims to reduce quality costs while expanding coverage and accelerating release velocity. With automation and manual tests only being applied where they are the optimal choice, we reduce the maintenance costs associated with automated tests while keeping our permanent staff small and nimble. While we retain a small, dedicated team of testers, additional testers for location, language, and device testing are available on short notice and for short time frames. Making closer ties between DevOps and quality systems improves the pipeline for continuous integration/deployment (CI/CD).
When to use automation
Automated tests get a lot of good press for their speed, repeatability, and low labor cost, but they aren’t perfect for every application. When applied to stable code paths with predictable outputs, automation can keep track of completed work and see that new work doesn’t impact it. But it’s essential to be sure failed or flakey tests are looked at immediately. Leaving an unreliable test in your process reduces your confidence in product quality without returning any benefit.
Three areas that benefit from automated testing include:
Unit tests
These run quickly and are tightly coupled with the code, even to the extent of being typically written in the same language. Best practices include breaking down unit testing into small parts reducing intermittent errors and run time. The smaller the amount of code covered, the more focused the test is and the easier it is to diagnose failures.
API tests
Application Program Interfaces (APIs) represent the communication channels between different parts of an application. API tests simulate signals from another part of the application to the part under test, sending a request that will produce a predictable response. Testing business logic with API tests goes quickly, though not as fast as unit tests, and is considered very reliable with few false positives for failures.
UI tests
User Interface (UI) tests approach testing like human testers, using the UI to send user commands to the program. The tools to perform this testing are designed for testers without programming experience and can be created to map to manual tests already in place. As the application becomes more stable, these automated UI tests can replace manual tests, freeing up your testers to concentrate on new areas under development.
Automated testing challenges
While correctly used automated testing can speed up and streamline your process, some obstacles remain:
- Talent: Quality engineers (QEs, Testers who develop automated tests) can be challenging to find as they are in great demand.
- Bottlenecks: When automated tests break down, someone must investigate why they aren’t working. The time they spend investigating is not spent on developing new tests and can stop the deployment process.
- Missing obvious bugs: Automation can only catch problems it is designed to catch, while it can miss failures a human tester with a real device would spot immediately. This results in false positives.
- Management of integration: Integrating additional code for automated testing requires extra management effort.
- Governance: Not all automation provides benefits, so oversight of writing, implementing, and maintaining tests is required to ensure cost-effectiveness.
When to use manual testing
After hearing about all the advantages of automated testing, you may wonder why you need manual testers. While automated tests run fast, developing one isn’t nearly as quickly as asking a manual tester to check a feature. This flexibility comes into play when verifying new features and producing reproducible steps in bugs.
Exploratory: Exploratory testing lets testers be detectives, investigating where the bugs can hide in the corners of design documents. Structured exploratory testing keeps your testers focused on specific areas while uncovering bugs automated scripts missed.
Usability: Usability testing focuses on how the user interacts with the application. This is best performed with real devices and in real locations. Testers look for where the customer experience doesn’t meet expectations. Test solutions should include management, planning, recruitment, recordings, and recommendations.
Explore the hidden costs of skipping usability testing
Localization: When software is translated into other languages, it’s best if testers look for more than just a foreign language. An expert global test network can check graphical or UI elements for cultural, language, or preferred device incompatibility.
Manual testing challenges
Although manual testing addresses several issues, there are still challenges to overcome:
- Efficiency: Manual testing is ill-suited to daily unit, API, and stable UI testing. Use automation to gain efficiency.
- Labor: Manual testing requires more labor than executing automated testing.
- Sourcing: Finding QA in-house or outsourcing for global localization can be difficult.
- Unskilled: Using testers without sufficient skill will result in more low-quality bugs being found.
- Strategy: Strategy, planning, management, and expertise are required to improve the end-to-end experience.
On-demand and full-time staffing models
Instead of relying only on a permanent, static test team, you can vary your staff size based on your needs. A more minor dedicated team can be augmented by on-demand testers to work when you require them. Testing for mobile apps, localized releases, payment gateway updates, and significant digital events all benefit from using on-demand testing to increase capacity.
Benefits of fused testing
Fused testing can leverage hybrid nearshore, onshore, and offshore resources, reducing effective hourly costs for quality personnel. Using a service such as Testlio can provide access to 1,200+ device types, 150+ countries, 100+ languages, and 50+ payment systems. You can tune your coverage to exactly what, when, and where you need it.
Techniques like parallel testing, global teams, overnight runs, weekend testing, and rapid initiation can improve quality process turnarounds, enabling faster release times. Clients using fused testing regularly see 4.8+ scores on app rating sites, high NPS scores, and positive NRR.
DevOps tracks your system’s stability and efficiency but can be coupled with testing management systems for signal-driven testing. Reporting customer support requests, third-party ratings, feature flag status, and more can help your test organization drive focused testing. Staying with the cutting edge of automation technology allows you to transform your SDLC into a more streamlined and efficient process.
Fused testing use cases
A few of the testing scenarios that benefit from a fused software testing approach include:
Native App testing: iOS, Android, OTT, and wearable technology often operate on episodic, 1-4 week releases, allowing the hybrid automated/manual testing with burstable test resources to shine.
Build testing: As your build process runs, it can interface with QA systems to start automated testing and signal manual testers as build criteria are met.
Payments testing: Global testing resources can ensure your application accepts a variety of payment systems around the world.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about payments testing, including test strategies, use cases, and what to expect for results.
Localization testing: Testing in native languages and locations worldwide helps you verify your application’s functionality in all the areas in which it will be deployed.
Stream testing: Confirming streaming data arrives without lag, loss, crashes, or glitches will satisfy your customers while tracking advertising and analytics to help your partners.
Role testing: Some software offers two or more different configurations, such as a buyer and a seller or a driver and a passenger. On-demand test teams can check both sides of the equation.
Fused testing and continuous integration: When you plan to utilize CI/CD for the fastest deployments, you need fused testing in these areas:
Building blocks of fused software testing
People
Modern quality expectations demand a team of experienced and varied professionals with a deep understanding of your product.
Methodologies
Five critical methodologies: burstable, collective, nearshore, crowdsourced, and outsourced testing.
Systems
Your testing tools and platforms must fit seamlessly into a modern DevOps architecture.
Fused Testing APIs
Fused testing APIs available from Testlio ensure the speed, efficiency, and traceability needed for your software engineering teams.
Instead of debating between different test strategies, switch to a fused testing approach leveraging the best automation and manual tests, the advantages of a dedicated team and additional on-demand testers, and the integration tools needed to direct your QA organization based on signals from your DevOps system. Improve your efficiency, your ROI, and your customer satisfaction all at once. There’s never been a better time to boldly go and adopt fused testing.

