Localization Testing Best Practices
Did you know that users worldwide downloaded approximately 77 billion mobile apps in 2023?

With the rise of global digital markets and a growing smartphone user base, making your app stand out requires more than great functionality. It demands cultural relevance and linguistic accuracy.
Global app developers must ensure their app is accessible to all types of users regardless of language and location. However, successfully adapting a product to a different language and locale can be challenging.
Localization testing is essential to overcome localization challenges. It ensures your app adapts to the cultural, linguistic, and regulatory needs of various markets. With growing user expectations, effective localization can distinguish between a successful global rollout and missed opportunities.
In this article, we will discuss some localization testing best practices and present a checklist to guide your testing efforts.
What is Localization Testing, and why is it important?
Localization testing is a software testing technique used to ensure that a product is suitable for a specific region, locale, or culture. This involves verifying that the software behaves correctly with the target audience’s language, cultural norms, and other regional settings.
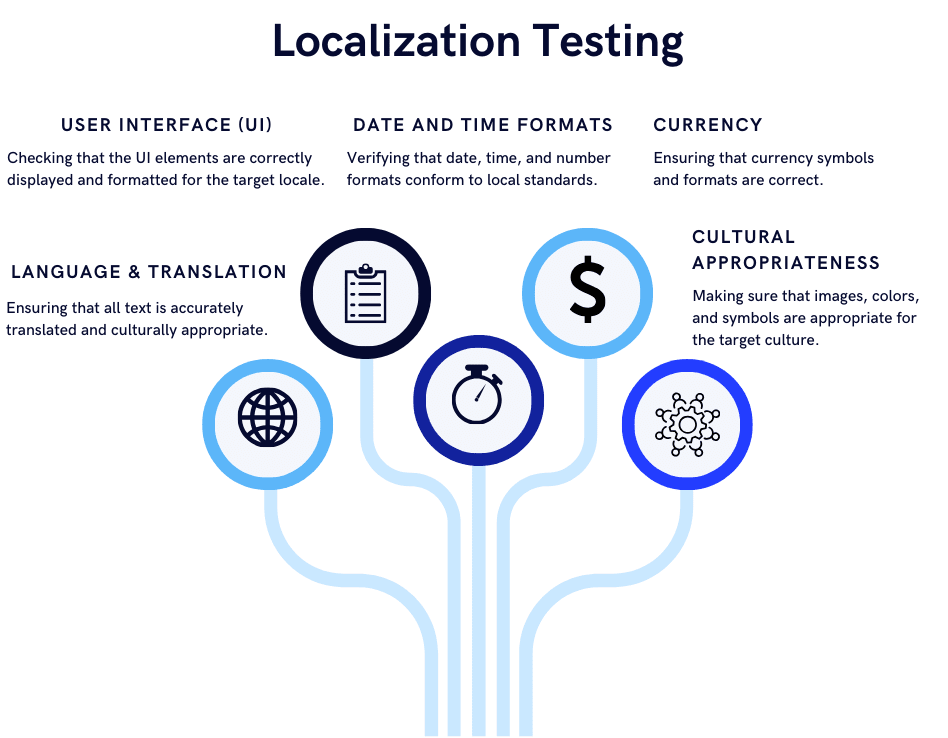
A localization test is crucial for any global business, as it guarantees not only that the product will work, but also that it will be culturally and linguistically appropriate.
Here are some reasons why localization testing is important:
- User Experience: It improves the user experience by making the software feel native to the user, which can increase user satisfaction and adoption rates.
- Market Reach: It allows companies to expand their market reach by making their products accessible to a global audience.
- Compliance: It verifies that the software complies with local regulations and standards, which can vary significantly between regions.
- Brand Image: It helps maintain a positive brand image by avoiding cultural mistakes and making sure that the product is well-received in different markets.
What Elements Should Be Considered for a Successful Localization Strategy?
Building a strong localization strategy requires careful planning and consideration. Here are five essential tips to create a solid framework:
1. Identify Target Regions
- Understand users’ characteristics, including product usage patterns and geodemographics.
- Take note of special seasons and public holidays.
- Analyze competitor characteristics, such as user base, growth, and product format (language, layout, and content).
- Assess your product’s features and the adjustments needed for localization.
2. Determine Localization Variables
- For content localization, go beyond language; consider local regulations, user content interests, and social, religious, and political norms.
- Maintain quality throughout the entire product localization process.
3. Plan Your Localization Timeline
- Remember, localization is an ongoing process that involves continuous quality improvements.
- Decide if you will implement a localized marketing strategy alongside your product localization.
4. Set Localization KPIs
Use the following performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your efforts:
- On-time delivery rate (%)
- Localization-related complaints (%)
- Localization-related bugs (%)
- Fixed localization bugs (%)
- Failed localization bugs (%)
- Number of users post product localization
5. Define Budget and Stakeholders
- Assign a project manager and team members, including the technical team.
- If in-house capacity is lacking, consider partnering with a software testing company like Testlio, which offers a global network of expert testers in over 150 countries. Partnering with an external translation company and a testing partner can ensure that your app meets the needs of global audiences.
6. Define Tools for Managing Strings in Translation Memory (TM)
- Ensure push/pull string extraction through automation. Set up automated scripts to extract new or modified strings during the build process and push them to the TM system. Once translations are completed or updated in the TM system, they should be automatically pulled back into the codebase.
- Maintain version history for translated strings, allowing teams to track changes over time.
- Incorporate localization tasks into the CI pipeline, such as validating that all required translations are present or checking for untranslated strings.
Top 8 Localization Best Practices
Localization is a crucial process for adapting your content, products, or services to meet the specific needs of different regions and cultures.
Here are best practices for ensuring effective localization and the importance of testing as a supportive measure.
1. Understand Your Target Audience
Conduct thorough research on cultural nuances and preferences in your target markets. Localizing your products or services requires understanding how different regions view them.
You’ll get higher engagement and conversion rates if you tailor content to resonate with local audiences.
2. Create a Style Guide
Develop a comprehensive style guide that outlines localized rules for language use, formatting, and tone. The guide should include specifics on date formats, currency symbols, and terminology variations across different locales. A consistent style guide helps maintain brand voice while ensuring cultural relevance.
3. Adjust Design Elements
Be mindful of design adjustments needed for different locales. Avoid using images with embedded text, as they complicate the localization process. Instead, use captions or overlays for text, allowing for easier translation and adaptation of visual elements to fit cultural contexts.
Additionally, ensure that your design accommodates various text lengths that may arise from translation.
4. Use Efficient Translation Tools
Select appropriate tools and software for managing translations effectively. These tools can streamline the localization workflow, making it easier to track changes and updates across multiple languages. Consider platforms that support collaboration among teams working in different time zones.
Make it easy for users to switch between languages on your website or application. Clear language options improve user experience and allow individuals to engage with your content in their preferred language, increasing accessibility and satisfaction.
5. Implement Internationalization (i18n)
Prepare your content for localization through internationalization. The process involves separating the translatable content from the logic of your application so that translations will be easier without requiring extensive rework.
Proper internationalization lays the groundwork for a smoother localization process and minimizes technical issues during translation.
6. Use Full Locales
Always specify a full locale instead of just a language. A full locale includes both the language and the country code (e.g., fr-FR for French in France). This precision allows your application to accommodate regional differences in spelling, date formats, and other cultural nuances.
As a result, you provide a better user experience and prevent misunderstandings that can arise from generic language settings.
7. Test Localizability Early and Often
Tests are typically associated with localization testing, but they play an important role throughout the entire localization process. Identify potential issues early on by regularly evaluating localized content for accuracy, cultural relevance, and usability.
This proactive approach helps refine content before it reaches end-users, ensuring a smooth experience across different markets
8. Prioritize International SEO
International SEO is necessary for increasing visibility in local search engines. Conduct keyword research specific to each locale to ensure that your content ranks well in local searches.
This practice not only drives traffic but also improves user experience by connecting users with content that meets their search intent.
Example of Localization Done Well
Let’s consider an e-commerce platform initially designed for English-speaking users in the United States. When localizing this platform for the Brazilian market, several key areas must be addressed to create a smooth and culturally relevant shopping experience.
The key areas include:
- Language and Dialect Adaptation: Translate content into Brazilian Portuguese, considering regional dialects and colloquialisms.
- Culturally Relevant Promotions: Align promotional campaigns with local holidays and events like Carnival and Black Friday.
- Payment Methods: Integrate local payment methods and local currency such as Boleto Bancário and Pix, along with traditional credit cards.
- Shipping and Delivery Options: Adapt shipping options to local logistics, offering various delivery methods and reliable tracking.
- Localized User Interface: Modify the UI to include Brazilian Portuguese text, ensuring clarity and usability.
- Cultural Sensitivity in Marketing: Use culturally relevant imagery and messaging featuring local influencers and familiar settings.
- Customer Support in Local Language: Provide customer support in Brazilian Portuguese through chat, email, and phone.
- Incorporation of Local Trends: Highlight local products or brands and collaborate with Brazilian artisans to appeal to national pride.
Testing for Localization
Localization testing is a critical process that ensures software applications are appropriately adapted for specific locales, considering language, culture, and regional requirements.
This testing verifies that the application functions correctly and resonates with local users, improving their overall experience.
Below are key methodologies involved in effective localization testing.
- Smoke Testing: Conduct initial checks on the software build to ensure business critical functionality & strings are localized before proceeding with more detailed testing.
- Functional Testing: Execute standard functional tests to verify that all features work correctly in the localized version of the application.
- Regression Testing: Perform regression tests to confirm that recent changes or fixes have not adversely affected existing functionalities.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve in-market users in testing to gather feedback on usability and cultural fit, ensuring that the application meets their expectations.
- Automation Testing: For large-scale projects, consider automation tools to streamline repetitive testing tasks, allowing for quicker turnaround times while maintaining accuracy.
Localization Testing with Testlio
Effective localization testing delivers a smooth user experience across diverse regions. Accurate translation, cultural relevance, and customized UIs can help you ensure your app resonates with users in every market.
Don’t let poor localization hold you back. Consider Testlio localization testing services to optimize your app’s localization!
Here’s what Testlio offers:
- Quicker and more reliable releases with our dedicated testing teams.
- Access to over 10,000 expert testers across 150+ countries.
- Testing of over 600,000 devices and 800+ payment methods to ensure your app performs flawlessly.
- Flexible staffing options to help you scale your resources based on your project needs.
- Rapid market expansion to expand into new markets with confidence.

Talk to an expert at Testlio today to learn how we can help you explore new markets and enhance your global presence.
